Scientists have created a new way to detect the proteins that make up the pandemic coronavirus, as well as antibodies against it.
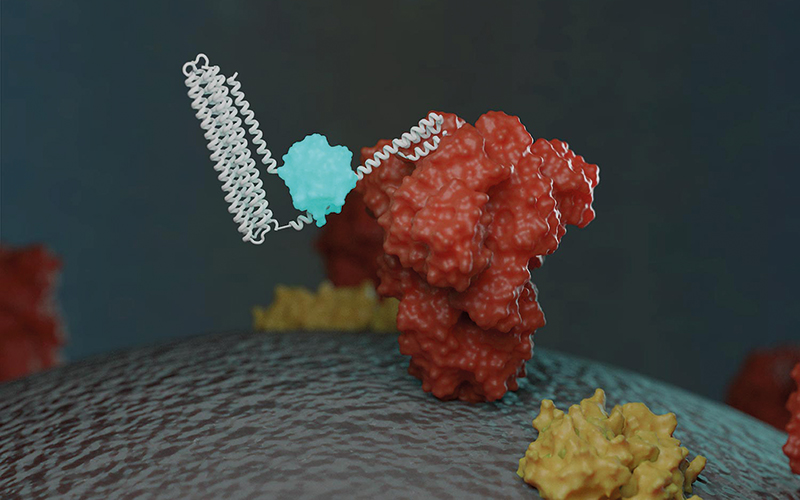
They designed protein-based biosensors that glow when mixed with components of the virus or specific COVID-19 antibodies. This breakthrough could enable faster and more widespread testing in the near future.
To diagnose coronavirus infection today, most medical laboratories rely on a RT-PCR, which amplifies genetic material from the virus so that it can be seen.
This technique requires specialised staff and equipment. It also consumes lab supplies that are now in high demand all over the world.
In an effort to directly detect coronavirus in patient samples without the need for genetic amplification, a team of researchers led by David Baker, Professor of Biochemistry and Director of the Institute for Protein Design at UW Medicine, used computers to design new biosensors.
These protein-based devices recognise specific molecules on the surface of the virus, bind to them, then emit light through a biochemical reaction.
“We have shown in the lab that these new sensors can readily detect virus proteins or antibodies in simulated nasal fluid or donated serum,” said Baker. “Our next goal is to ensure they can be used reliably in a diagnostic setting.”